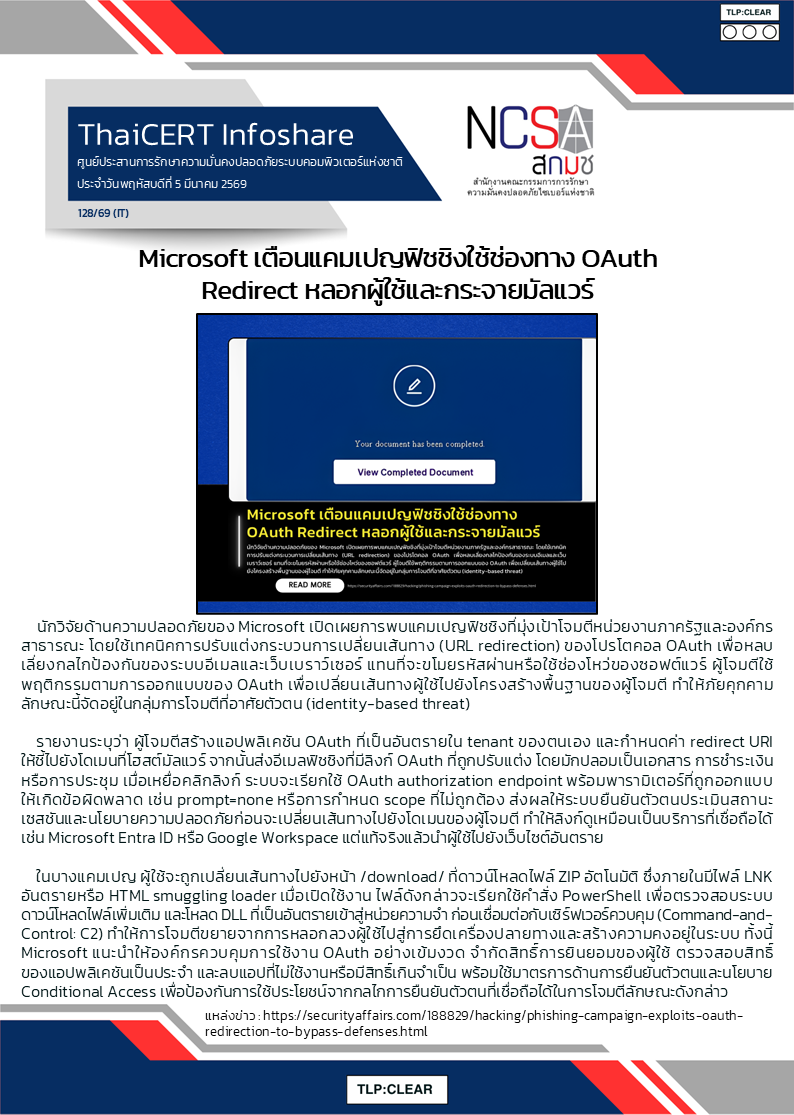
️ ThaiCERT ได้ติดตามสถานการณ์ภัยคุกคามทางไซเบอร์ และพบประกาศด้านความมั่นคงปลอดภัยจาก WatchGuard เกี่ยวกับช่องโหว่ CVE-2026-3342 ซึ่งเป็นช่องโหว่ประเภท Out-of-bounds Write ใน WatchGuard Fireware OS โดยอาจเปิดโอกาสให้ ผู้โจมตีที่ยืนยันตัวตนแล้วและมีสิทธิ์ผู้ดูแลระดับ privileged administrator สามารถใช้ management interface ที่เปิดเข้าถึงได้ เพื่อ รันโค้ดด้วยสิทธิ์ root บนอุปกรณ์ที่ได้รับผลกระทบ ส่งผลให้มีความเสี่ยงสูงต่อการถูกยึดระบบหรือแก้ไขการตั้งค่าความมั่นคงปลอดภัยของอุปกรณ์.
️ ThaiCERT ได้ติดตามสถานการณ์ภัยคุกคามทางไซเบอร์ และพบประกาศด้านความมั่นคงปลอดภัยจาก WatchGuard เกี่ยวกับช่องโหว่ CVE-2026-3342 ซึ่งเป็นช่องโหว่ประเภท Out-of-bounds Write ใน WatchGuard Fireware OS โดยอาจเปิดโอกาสให้ ผู้โจมตีที่ยืนยันตัวตนแล้วและมีสิทธิ์ผู้ดูแลระดับ privileged administrator สามารถใช้ management interface ที่เปิดเข้าถึงได้ เพื่อ รันโค้ดด้วยสิทธิ์ root บนอุปกรณ์ที่ได้รับผลกระทบ ส่งผลให้มีความเสี่ยงสูงต่อการถูกยึดระบบหรือแก้ไขการตั้งค่าความมั่นคงปลอดภัยของอุปกรณ์.
-
รายละเอียดช่องโหว่
CVE-2026-3342 - Out-of-bounds Write in WatchGuard Fireware OS (CVSS v3.1: 7.2)
ช่องโหว่นี้เกิดจากการเขียนข้อมูลเกินขอบเขตหน่วยความจำและอาจทำให้ผู้ดูแลระบบที่ผ่านการยืนยันตัวตนแล้ว สามารถ execute arbitrary code with root permissions ผ่าน exposed management interface ได้ -
ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ได้รับผลกระทบ
- Fireware OS 11.9 ถึง 11.12.4_Update1
- Fireware OS 12.0 ถึง 12.11.7
- Fireware OS 2025.1 ถึง 2026.1.1
- แนวทางการแก้ไข
- อัพเดท Fireware OS 2026.1.2
- อัพเดท Fireware OS 12.11.8
- สำหรับ Fireware OS 12.5.x (T15 & T35 models) ให้อัปเดตเป็น 12.5.17
- สำหรับ Fireware OS 11.x ผู้ผลิตระบุว่าเป็น End of Life แล้ว จึงควรวางแผนอัปเกรดหรือเปลี่ยนทดแทนโดยเร็ว.
-
หากยังไม่สามารถอัปเดตได้ ควรดำเนินการดังนี้
ไม่มี workaround สำหรับช่องโหว่นี้ควรรีบดำเนินการอัพเดทโดยด่วน -
แหล่งอ้างอิง











 แหล่งอ้างอิง:
แหล่งอ้างอิง: 




 ขอให้ผู้ใช้งาน Android ตรวจสอบและอัปเดตอุปกรณ์โดยเร็ว เพื่อลดความเสี่ยงจากการถูกโจมตี
ขอให้ผู้ใช้งาน Android ตรวจสอบและอัปเดตอุปกรณ์โดยเร็ว เพื่อลดความเสี่ยงจากการถูกโจมตี